TYPES OF COMPUTER
Supercomputer:
A supercomputer is a computer with a raised degree of execution when it appeared differently in relation to a comprehensively helpful computer. The presentation of a supercomputer is consistently assessed in floating-point undertakings consistently (FLOPS) as opposed to million bearings for each second (MIPS). Since 2017, there are supercomputers that can perform over a hundred quadrillion FLOPS (petaFLOPS). Since November 2017, the aggregate of the world's quickest 500 supercomputers run Linux-based working systems. Additional examination is being driven in China, the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, and Japan to manufacture significantly faster, logically astounding and precisely prevalent exascale supercomputers.
Supercomputers accept a critical activity in the field of computational science and are used for a wide extent of computationally gathered tasks in various fields, including quantum mechanics, atmosphere evaluating, climate research, oil and gas examination, sub-nuclear showing (processing the structures and properties of substance blends, regular macromolecules, polymers, and jewels), and physical reenactments, (for instance, generations of the early depictions of the universe, plane, and transport ideal structure, the blast of nuclear weapons, and nuclear mix). Since their commencement, they have been fundamental in the field of cryptanalysis.
Supercomputers were exhibited during the 1960s, and for a drawn-out period of time, the quickest was made by Seymour Cray at Control Data Corporation (CDC), Cray Research and ensuing associations bearing his name or monogram. The primary such machines were significantly tuned customary plans that ran speedier than their dynamically extensively valuable companions. Through the 1960s, they began to incorporate growing proportions of parallelism with one to four processors being ordinary. From the 1970s, vector processors taking a shot at gigantic assortments of data came to order. An exceptional model is the significantly compelling Cray-1 of 1976. Vector computers remained the transcendent arrangement during the 1990s. Starting there until today, gigantically parallel supercomputers with incalculable off-the-rack processors transformed into the standard
The US has for a long while been the pioneer in the supercomputer field, first through Cray's for all intents and purposes nonstop prevalence of the field, and later through a collection of development associations. Japan made huge strolls in the field during the 1980s and 90s, be that as it may, since, at that point, China has gotten continuously unique in the field. November 2018, the quickest supercomputer on the TOP500 supercomputer list is the Summit, in the United States, with a LINPACK benchmark score of 143.5 PFLOPS, trailed by, Sierra, by around 48.860 PFLOPS. The US has five of the fundamental 10 and China has two. In June 2018, all supercomputers on the once-over joined broke the 1 exaFLOPS mark.
Centralized server computer:
These Server PCs are utilized essentially by colossal connections for basic applications; mass information taking care of, for example, enrollment, industry and client estimations, endeavor asset coordinating; and exchange getting ready. They are bigger and have more processing power than some various classes of computers: minicomputers, servers, workstations, and PCs.
The term at first alluded to the enormous cabinets called "centralized servers" that housed the central processing unit and guideline memory of early computers. A while later, the term was used to perceive generally excellent quality business machines from less noteworthy units. Most enormous scale computer system models were developed during the 1960s, yet continue creating. Centralized computer computers are much of the time used as servers.
Server Computer:
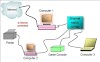
A server is a central computer that contains collections of information and tasks. Furthermore called a framework server, this structure empowers each and every related client to share and store electronic information and applications. Two noteworthy sorts of servers are archive servers and application servers.
Servers are a phase under supercomputers since they don't focus on endeavoring to fathom one complex issue anyway endeavor to tackle numerous relative tinier ones. An instance of servers would be the computers that Wikipedia stores its reference book on. Those computers need to continue to find the page you're scanning for and send it to you. In itself, it is definitely not a significant endeavor, yet it transforms into a livelihood for a server when the computers need to continue to find lots of pages for some people and send them to the ideal spot. A couple of servers, similar to the ones Google uses for something like Google Documents, have applications on them instead of just records, like Wikipedia.
In setting up, a server is a PC program or a contraption that offers an incentive to different exercises or devices, called "clients". This structure is known as the client-server model, and a singular generally speaking estimation is disregarded on various techniques or contraptions. Servers can give different functionalities, regularly called "organizations, for instance, sharing data or resources among numerous clients or playing out the estimation for a client. A solitary server can serve numerous clients, and a solitary client can use various servers. A client technique may run on a comparable gadget or may interface over a framework to a server on a substitute gadget. Regular servers are database servers, record servers, mail servers, print servers, web servers, game servers, and application servers.
Client-server structures are today practically sometimes realized by (and frequently identified with) the sales response model: a client sends a sales to the server, which plays out some action and sends a response back to the client, typically with a result or insistence. Allocating a PC as "server-class hardware" derives that it is explicit for running servers on it. This regularly construes it is more predominant and strong than standard PCs, yet then again, huge processing gatherings might be made out of various by and largely clear, replaceable server fragments.










Post a Comment
0 Comments